
Photo source:
Natural-Hormones.netEstrogens
Female: Menstrual cycle. Pregnancy.
Breast enlargement. Wide pelis.
Increased Height.
Male:???...
Estrogens are known as a female hormones. These are group of steroid hormones which are found to have estrogenic characteristics. Estrogens are found in the fat tissues, in the adrenal glands, placenta, in the corpus luteum and in the ovaries, which are stimulated by the Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and the Luteinizing Hormones (LH).
There are also trace amount of estrogen found in males. Estrogen plays a role in the maturation of sperms. Estrogen also regulates the production of cholesterole. It decreases the amount of plaque build up to prevent infarction.
Two types of EstrogensThere are different kinds of estrogens. Some are naturally occuring in the body and the others are either artificially produced or naturally occur in plants.
- Estrogens which are found in the body are known as the steroidal estrogens. There are three estrogens which are inherently found in women, These are Estradiol 17-B, Estrone and Estriol. Women who are not pregnant, Estrdiol 17-B is the hormone present. But as the woman ages and is in post menopausal stage, the Estradiol 17-B present is decreased and it is replaced by Estrone, which is weaker than Estradiol. The estrogen estriol is primarily produced by the placenta, therefore making it primarily the estrogen of pregnancy.
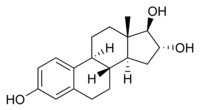 ESTRIOL
ESTRIOL
 ESTRADIOL
ESTRADIOL
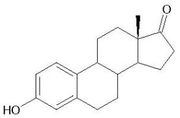 ESTRONE
ESTRONE
World of Molecules
- Other estrogens are produced artificially, or may be naturally occuring in nature. Though these may have estrogenic capabilities, these are not necessarily classified as steroids which are like the ones being produced by mammals. These are called the nonsteroidal estrogens. Examples of which is the estrogen produced by plants, which is also known as the phyto estrogen. Substances which are artificially produced are called xenoestrogens.
Functions of Estrogens
- It is responsible for the development of secondary characteristics in women.
- Responsible for burning of fats in metabolism.
- It is responsible for the thickening of the endometrium and vaginal walls.
- For the growth of the uterine.
- It increases the adhessiveness of the platelets.
- It decrease the LDL level and at the same time increasing the HDL level
- This is also plays a role in the wter and salt balance.
- In males, some reproductive functions are being regulated by estrogen for the maturation of sperms.
SpecimenA 24 hour urine or a venous blood is collected. Saliva may also be tested depending on the test requested by the physician.
Why test for Estrogen?
- It is tested to know if the woman has undergone the menopausal period.
- Determine if there is a problem in the fetus or in the mother's pregnancy.
- To detect if there is an abnormal level of hormones especially in girls who are enetering the puberty stage.
- To explain abnormally high production of estrogen level in males, which may give unusual sexual characteristics, and to know if there are problems in their organs such as the testicles, which may cause the production of tumor cells.
Clinical Significance:
Elevated level
Estradiol
- Liver problems in both male and female.
- It may indicate tumors of the adrenal gland in both male and female.
- Tumor in the ovaries in female. (it may also increase in females who are undergoing hormone therapy for the treatment of infertility.)
- In males, it may be indicated by testicular tumor.
Estriol
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Early puberty.
Decrease level
Estradiol
- This may indicate the female is in her menopausal period.
- Ovaries are not functioning well.
- Anorexia nervosa also cause a decrease in the level of estrogen.
Estriol
- In pregnant women, a sudden deacrease or if the level of estriol is low, it is an indicative of fetal and/or placental problems.
- Menopause.
Normal levels of Estrogen:
Children: 0-15 pg/ml or 0-55 pmol/L
Males: 10=50 pg/ml or 37-184 pmol/L
Females before menopausal period: 30-400 pg/ml or110-1,468 pmol/L
Females after menopausal period: 0-30 pg/ml or 0-110 pmol/L
In pregnant women:
At the first trimester: <>
At the second trimester: 38-140 ng/ml
At the third trimester: 31-460 ng/ml
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors which may affect the test:
- Diabetes.
- Drugs like clomiphene and steroids.
- Birth control pills.
- Hormonal Replacement therapy for females who are on the menopausal stage.
References:
Wikipedia
Healthy WomenLab Tests Online-FAQLab Tests Online-SAMPLEQuest Diagnostics
Diagnose-Me




